Work Packages
The Bifrost project is divided into 11 work packages of which two of them (WP 1 and WP 2) focus on project management, administration, and communication. In the following, you will find a short introduction to the focus of WP3-11.
Validation of Harald West storage potential and capacity (headed by TotalEnergies)
This work package describes activities performed in two stages:
A preliminary stage: to firstly confirm the storage potential of Harald West (sandstone). This stage also covers the assessment of the potential of other fields accessible through the Harald facility (Harald East chalk reservoir – studies under WP4) to provide an insight on the potential for storage capacity and allow for the sizing of the facilities. Furthermore, it covers a review of legacy wells with an assessment of potential integrity threats and remediation actions.
A conceptual stage: if preliminary study outcome is positive, TotalEnergies will carry out a more detailed and comprehensive evaluation of the risks and storage resources to support the selected development concept.
CO2 storage in Harald East chalk – subsurface studies (DTU offshore)
This work package describes the subsurface studies necessary to confirm the potential for CO2 storage in the Harald East chalk reservoir. Chalk is the predominant lithology for hydrocarbon fields in the Danish North Sea, however for CO2 storage purposes, chalk is seen as a less mature lithology than sandstone. CO2 storage in Harald East chalk would bring additional storage potential to Bifrost. Additionally, these studies could unlock a much larger CO2 storage potential in chalk in the Danish North Sea.
This work package builds on a State-of-the-Art study conducted by DTU Offshore and published in the report “CO2 storage in Danish Oil & Gas fields”, December 2020 (link to executive summary of the report in Danish here) and later published in the paper “Challenges and enablers for large-scale CO2 storage in chalk formations” (Bonto et al. 2021; link: doi.org/10.1016/j.earscirev.2021.103826). The report and paper provide a State-of-the-Art summary for CO2 storage in existing offshore DUC oil and gas chalk reservoirs and maps the knowledge and technology gaps that will be important to address for a dedicated CO2 storage project in Danish chalk to become feasible.
Well design and drilling (TotalEnergies)
This work package is dedicated to the design of Harald West wells upper and lower completion, ensuring consistency with reservoir injectivity and surface constraints under the assumption of a continuous injection flow of non-cryogenic pressurized CO2 at the wellhead. These injection conditions do not bear the shortcomings of batch CO2 injection which results in frequent expansion of CO2 during injection stops and the associated extreme low temperatures that pose threats to well integrity as well as flow assurance specific problems and operating challenges. The range for injection pressure conditions will be considered in coordination with subsurface work (WP03) to cover the anticipated re-pressurization of the reservoir during the life of the project.
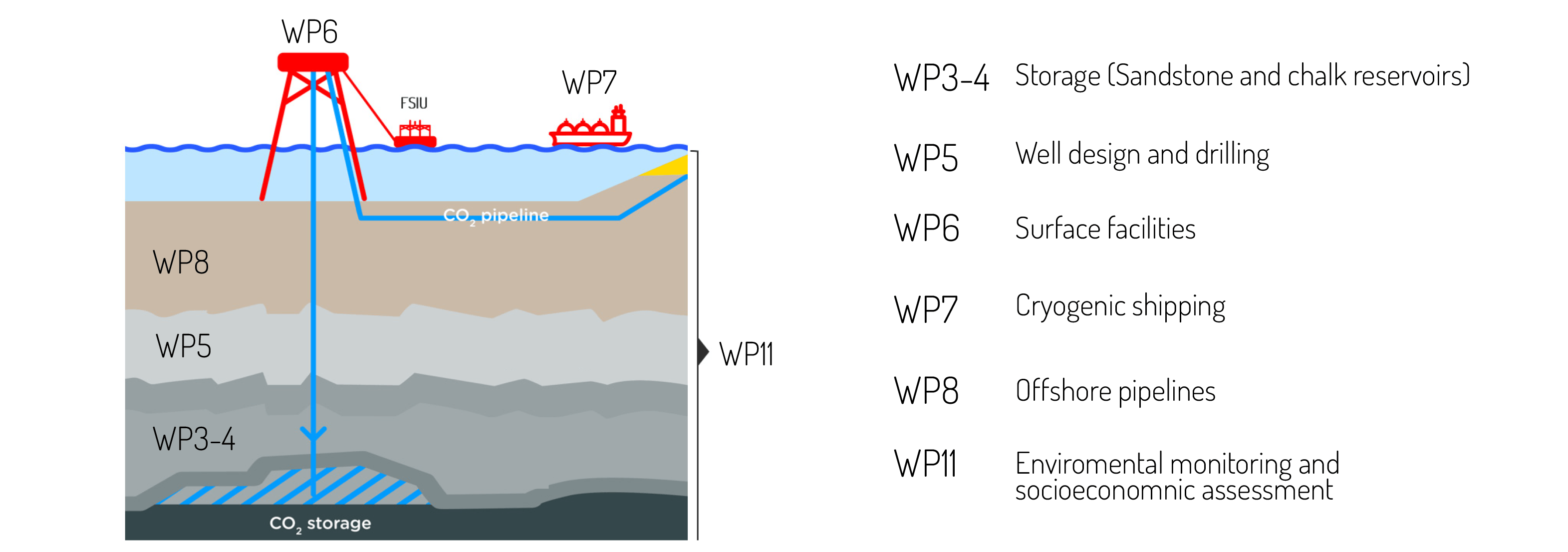
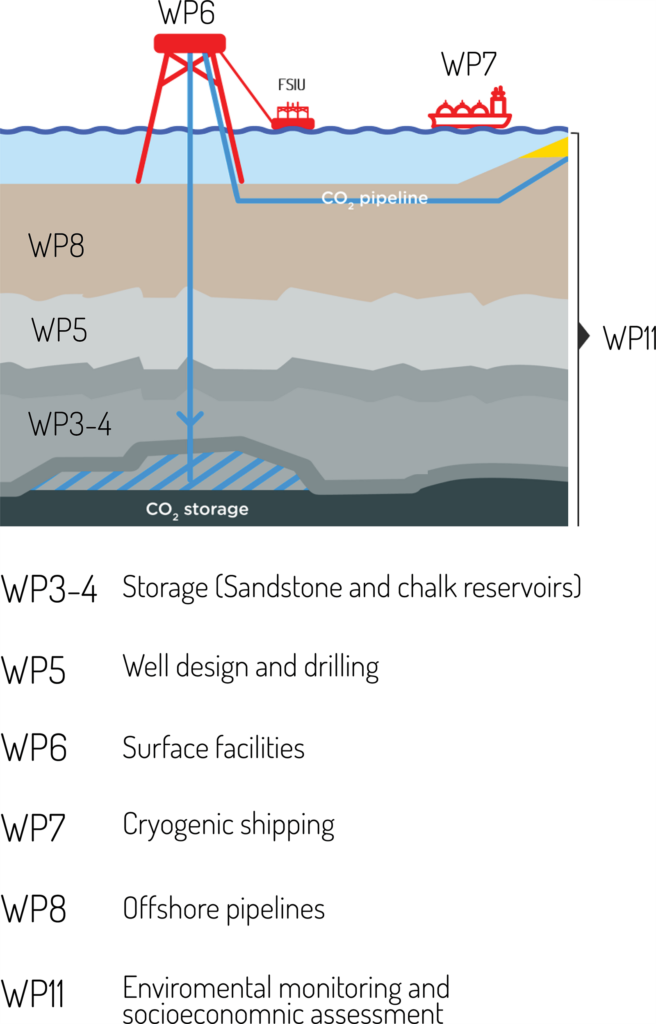
Surface facilities and operation (TotalEnergies)
This work package investigates the feasibility of a CO2 transportation and injection chain aiming at a continuous injection of CO2 via two platform wells into the Harald West reservoir. This chain comprises a fleet of medium pressure cryogenic shuttle tankers for offshore offloading, a floating unit for CO2 buffer storage and conditioning for injection, and integration modifications on the Harald West facilities.
Cryogenic CO2 shipping (TotalEnergies)
This work package is dedicated to the screening and selection of ship design and interface with the New Offshore Offloading Facility described in WP6.
The work performed capitalizes on experience gained from on-going projects – Northern Lights (Norway) and Aramis (the Netherlands). While ships for those projects are designed for onshore loading and onshore offloading, some incremental work is nevertheless required to assess suitability and potential design modification for offshore offloading in the frame of the full offshore concept studied in WP6.
Dynamic positioning capacities and bow off-loading requirements are key elements that are being investigated.
Offshore pipeline (Ørsted)
The re-use of existing pipelines is a key lever to optimize costs and reduce carbon footprint. Bifrost studies the potential re-use of the existing offshore hydrocarbon pipelines operated by Ørsted. The CO2 transported by ship would be offloaded at an onshore receiving terminal equipped with offloading facilities, buffer storage and compression stations to condition CO2 in dense phase before transportation through the offshore pipeline to the Harald West facilities.
Safety, Environment, Societal implications (TotalEnergies)
The new facilities and modifications to existing facilities investigated for project Bifrost shall be designed such that methods of risk reduction commonly used to ensure acceptable HSE performance and qualities are inherent in design, construction, commissioning and operation.
This is being done through:
- Implementing high HSE technical standards
- Defining permit and consent register in compliance with regulations in place
- Performing Environmental and Societal desktop study and SENVID study to identify social and environmental potential impact
Monitoring plan (DTU Offshore & TotalEnergies)
Monitoring of geological storage facilities, from pre-injection baseline surveys to final handover of the facility to authorities, is central to demonstrating safe and permanent containment, to prevent and mitigate potential leakage, and to build public acceptance. Identifying the right monitoring technologies is therefore key to the success of any CCS project. This work package includes activities to develop a CO2 monitoring strategy for project Bifrost to prepare for the elaboration of an actual monitoring plan:
- Review of ‘state-of-the-art’ within monitoring, measurement and verification (MMV) for offshore CO2 storage projects world-wide
- Development of concept for monitoring CO2 injection and storage in the Harald reservoirs – closely linked to the subsurface understanding gained from WP3 and WP4
- Maturation of two new innovative monitoring technologies at DTU Offshore, including highly sensitive, stationary, specific chemical sensors for continuous monitoring of the storage site, and a monitoring digital twin concept, utilizing an advanced machine learning method to optimize prediction of CO2 plume migration
Socio-economic and perception (DTU Management)
Acceptance of energy technologies are crucial in the green energy transition and lack of acceptance can be a game-stopper. Acceptance is strongly related to the perceived benefits (CO2 reductions, employment effects etc.) and costs/risks (leakages, environmental impact, and high costs etc.) associated with technologies. If the costs out-weights the benefits, people tend to dislike technologies. WP11 analyses the benefits and the costs of CCS and tests how benefit and cost information influence acceptance of, and preferences for, CCS.
The objectives are:
- To estimate the economic effects of CO2 storage on the Danish economy
- To gather and analyze perceptions and acceptance of carbon storage among key stakeholders
- To gather and analyze perceptions, acceptance of – and preferences for CO2 storage among the Danish general population and specifically targeted groups
A national survey reaching 50,000 Danish households and with over 8,000 respondents has been carried out together with dedicated stakeholder interviews to assess the perception & acceptance of CCS in Denmark. An additional survey is in the pipeline. Results of this will follow.