15 January 2026
| News article
Our mission is to establish Project Bifrost as a European hub for Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS). By implementing advanced technologies and fostering partnerships, we aim to reduce carbon emissions and support Europe’s low-carbon transition. We are committed to innovation and operational excellence for a sustainable energy future.
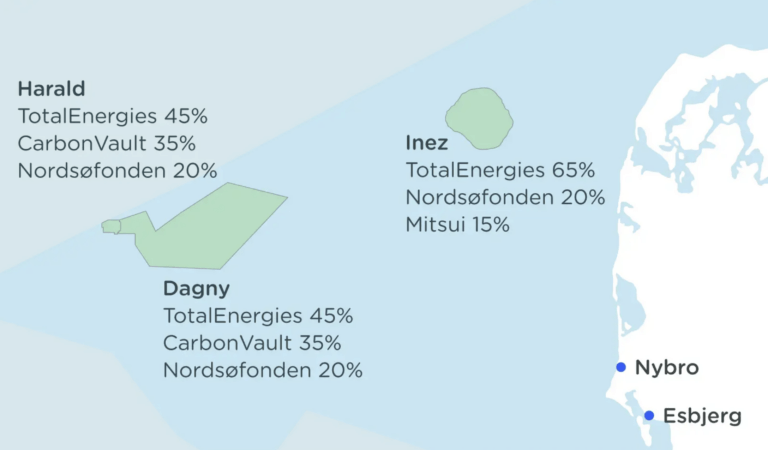



At TotalEnergies, we see CCS as a key component in the energy transition to NetZero. In Denmark, we have an ambitious vision to make the country a European hub for CO2 storage
Martin Rune Pedersen, Country Chair, TotalEnergies Denmark